1. Introduction
In recent years, the global financial landscape has been transformed by the rapid rise of digital currencies. Among these, Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) have emerged as a pioneering innovation, capturing the attention of governments, financial institutions, and technology experts alike. Unlike decentralized cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, CBDCs are state-controlled digital assets issued and regulated by central banks. As an increasing number of nations explore or adopt these government-backed digital currencies, it’s crucial to understand their far-reaching implications for the global economy.
This article delves into the core aspects of CBDCs, critically examining their potential benefits, key challenges, and future trajectory. We will analyze how CBDCs could revolutionize global trade, reshape financial regulation, and promote financial inclusion, as well as their impact on the banking sector, privacy rights, and governance frameworks.
2. What is a CBDC?
A Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) is a digital form of a country’s official currency, issued and controlled by the nation’s central bank. Unlike cryptocurrencies that operate on decentralized networks, CBDCs are fully regulated by governmental authorities, providing a secure and stable alternative to both traditional fiat currencies and decentralized digital currencies.
CBDCs can take several forms, from digital versions of cash to more complex blockchain-based structures. The key distinction is that they remain under the jurisdiction and control of the central bank, meaning they are more stable than cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, which experience volatility due to market forces.
3. The Global Shift Towards CBDCs
The global interest in CBDCs is accelerating as more central banks recognize the potential of these digital currencies to modernize financial systems. China has been a leader in this space with its digital yuan, while the European Central Bank and Bank of England are exploring their own initiatives. The U.S. Federal Reserve has also begun research into CBDCs, with the possibility of a digital dollar on the horizon.
This shift is driven by a variety of factors, including the need for faster payments, enhanced financial inclusion, and the desire to reduce reliance on cash. Additionally, central banks are looking to compete with the growing influence of cryptocurrencies and other private digital currencies.
Here’s an enhanced version of the text with more selective and specific words:
4. Benefits of CBDCs
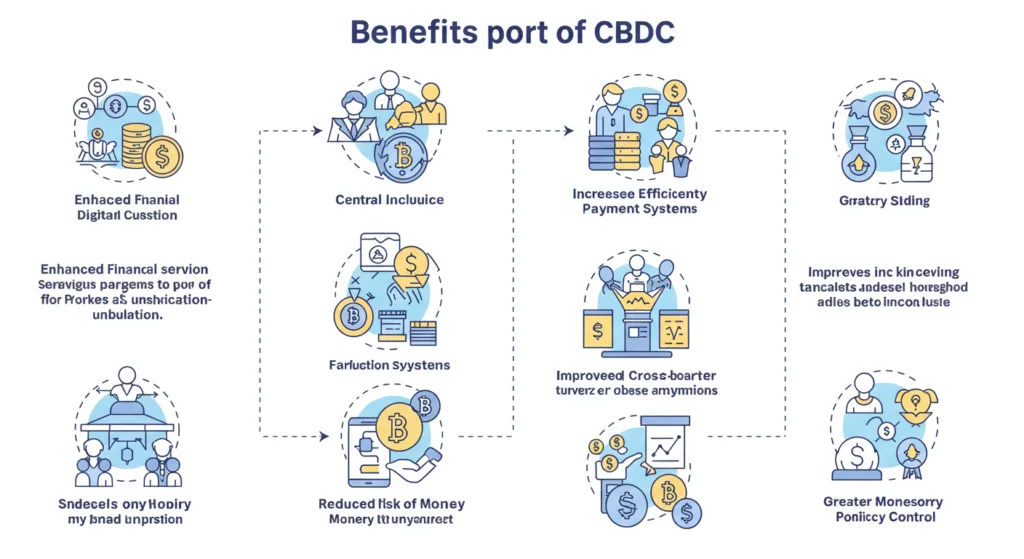
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) offer a range of transformative benefits that could fundamentally reshape the global financial ecosystem:
- Enhanced Efficiency: CBDCs significantly optimize payment systems, enabling faster, more cost-effective transactions. This is especially crucial for cross-border payments, which traditionally involve multiple intermediaries, resulting in delays and high fees.
- Financial Inclusion: Digital currencies can help integrate underserved and unbanked populations into the financial ecosystem. With the ubiquitous use of smartphones, individuals in rural, remote, or economically marginalized areas can now access critical financial services without the need for a traditional banking infrastructure.
- Lower Transaction Costs: By eliminating the need for intermediaries such as payment processors or correspondent banks, CBDCs can substantially reduce the costs associated with financial transactions, making digital payments more affordable and efficient for both consumers and businesses.
- Improved Monetary Policy Control: With CBDCs, central banks can enhance their ability to implement monetary policy. Direct control over the issuance and circulation of digital currencies allows central banks to exert greater influence over interest rates, inflation, and the money supply, thereby stabilizing the economy more effectively.
5. Challenges and Risks of CBDCs
While CBDCs offer exciting potential, there are several challenges and risks that must be addressed:
- Privacy Concerns: Since CBDCs are issued and controlled by central banks, there is concern about the level of surveillance and control that governments may exert over individual transactions. Striking a balance between privacy and transparency is critical to ensure public trust.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Digital currencies are vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Protecting the infrastructure that supports CBDCs will be essential to prevent hacks, data breaches, or other security risks.
- Technological Barriers: The implementation of CBDCs requires advanced technological infrastructure, which may be difficult for certain countries to develop. This poses a challenge, especially for developing economies.
- Impact on the Banking Sector: The introduction of CBDCs could disrupt the traditional banking system. If consumers hold their digital currencies directly with central banks, commercial banks may face challenges in maintaining their role as intermediaries.
6. CBDCs and Their Technological Foundations
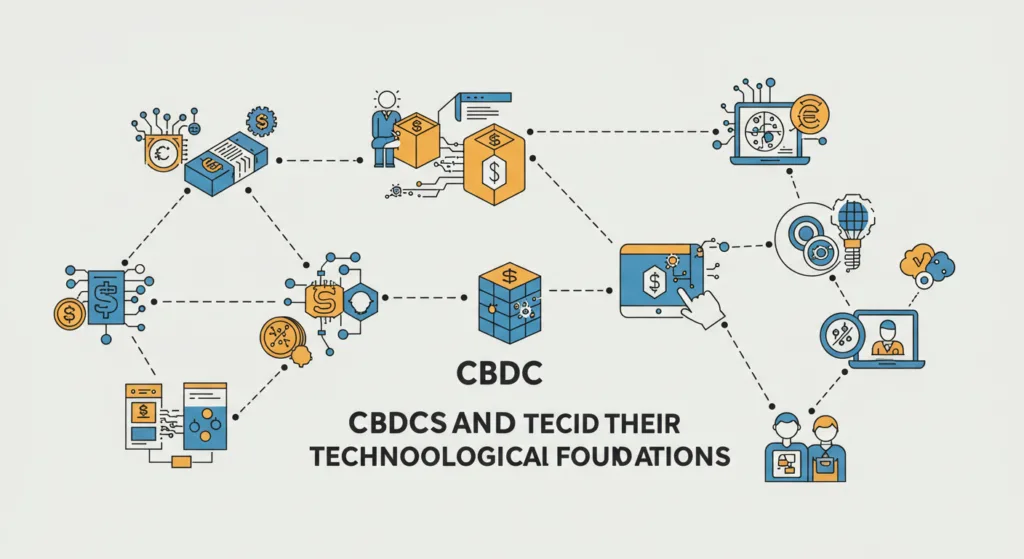
The underlying technology of CBDCs is critical to their design and functionality. Many CBDCs are built on blockchain or similar distributed ledger technologies (DLT), which provide transparency, security, and immutability. Blockchain enables the secure transfer of assets without the need for a central authority, making it an ideal platform for digital currencies.
Additionally, encryption plays a vital role in safeguarding transactions and ensuring the integrity of digital currency networks. The use of cryptographic techniques ensures that each transaction is secure and cannot be tampered with, enhancing trust in CBDCs.
7. CBDCs vs. Cryptocurrencies: Key Differences
While both CBDCs and cryptocurrencies are digital currencies, they differ significantly in terms of governance, stability, and decentralization.
- Centralization vs. Decentralization: CBDCs are centrally controlled by governments or central banks, while cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are decentralized and operate on blockchain networks without a central authority.
- Stability: CBDCs are designed to be stable, as they are backed by a country’s economy. In contrast, cryptocurrencies can experience extreme volatility due to speculative trading and market forces.
- Regulation: CBDCs are subject to government oversight and regulatory frameworks, while cryptocurrencies often operate in a less regulated environment, depending on the jurisdiction.
8. How CBDCs Could Transform the Banking Sector
The introduction of CBDCs could have profound implications for the banking sector. Traditional banks may face increased competition from central banks, as individuals and businesses may prefer to hold digital currencies directly with the central bank. This could lead to a shift away from traditional deposit-taking functions of banks.
On the other hand, banks could find new opportunities in the digital currency ecosystem, such as offering services related to CBDC transactions, wallets, and cybersecurity. As such, banks will need to adapt and innovate in response to the rise of CBDCs.
9. CBDCs and Global Trade
CBDCs could greatly enhance global trade by making cross-border payments faster, cheaper, and more transparent. Today, international transactions are often slow, requiring multiple intermediaries and subject to high fees. With CBDCs, these processes can be simplified, reducing the cost and time associated with sending money across borders.
Additionally, CBDCs could improve exchange rate stability by providing a more reliable and transparent mechanism for currency conversion, benefiting businesses engaged in international trade.
10. CBDCs in Financial Regulation

As governments and regulators look to create a stable financial environment, CBDCs offer a new tool for financial regulation. By issuing digital currencies, central banks can have a direct influence on monetary policy, including interest rates and money supply.
CBDCs could improve anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) regulations by making digital currencies easier to track and monitor than physical cash.
11. The Role of CBDCs in Financial Inclusion
One of the most significant benefits of CBDCs is their potential to promote financial inclusion. Many people around the world remain unbanked or underbanked, lacking access to traditional financial services like savings accounts, loans, or credit.
CBDCs, however, can enable people in remote or underserved areas to access financial services directly through their smartphones. By providing a more inclusive alternative to traditional banking, CBDCs can help bridge the financial gap and promote economic development.
12. Governance and Control of CBDCs
Governance plays a crucial role in ensuring that CBDCs are effectively managed and aligned with national interests. Central banks are primarily responsible for issuing and regulating CBDCs, but questions around how they should be governed, who controls the supply, and how they interact with commercial banks remain critical.
Some countries may opt for a centralized governance model, where a single central bank has full control, while others may explore decentralized governance structures involving multiple stakeholders.
13. The Role of CBDCs in International Monetary Systems
CBDCs could have a significant impact on international monetary systems. For instance, they could help stabilize exchange rates, reduce reliance on traditional reserve currencies like the U.S. dollar, and provide an alternative to unstable national currencies.
If widely adopted, CBDCs could transform the global financial architecture, allowing countries to more easily settle international transactions and trade, reducing the need for foreign exchange intermediaries.
14. CBDCs and Privacy Concerns

One of the most significant concerns surrounding CBDCs is the issue of privacy. Since CBDCs are digital and centrally controlled, they could potentially enable governments to monitor every transaction. While transparency is essential for preventing illegal activities, there is a delicate balance to be struck between privacy and surveillance.
To mitigate privacy concerns, it is crucial to implement strong data protection mechanisms and ensure that consumers’ personal information is kept secure. Blockchain-based solutions may offer a way to safeguard privacy while maintaining transparency.
15. The Future Impact of CBDCs on the Cryptocurrency Market
The rise of CBDCs could have profound implications for the broader cryptocurrency market. While CBDCs are centralized and controlled by governments, they may challenge decentralized cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, which are not subject to central authority.
However, rather than replacing cryptocurrencies, CBDCs may coexist alongside them, offering a stable alternative for users who prefer government-backed digital currencies, while cryptocurrencies continue to appeal to those seeking decentralization and privacy.
16. Conclusion: The Future Outlook of CBDCs
As the world moves towards a more digital future, Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are poised to play a crucial role in shaping the global financial landscape. While challenges remain, particularly in terms of privacy, cybersecurity, and regulation, the potential benefits of CBDCs – including increased efficiency, financial inclusion, and better monetary policy implementation – are immense.
The future of CBDCs is promising, and their impact on the global financial system will continue to evolve as more countries explore their adoption. It is clear that CBDCs are not just a passing trend but a fundamental shift in how we understand and use money.